Page 151 - FRUTAS DEL TRÓPICO
P. 151
intRoduction to teRminology and techniques foR studying enviRonmental
physiology of subtRopical and tRopical fRuit cRops 151
oxygenase, the first enzyme of the photosynthetic carbon fixation cycle (the Calvin Cycle).
Therefore, root restriction in mangos was presumably limiting photosynthesis due to a reduc-
tion of stomatal conductance and not biochemical mechanisms.
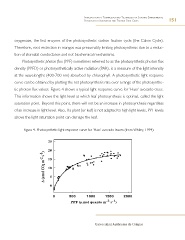
Photosynthetic photon flux (PPF) sometimes referred to as the photosynthetic photon flux
density (PPFD) or photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), is a measure of the light intensity
at the wavelengths (400-700 nm) absorbed by chlorophyll. A photosynthetic light response
curve can be obtained by plotting the net photosynthesis rate over a range of the photosynthe-
tic photon flux values. Figure 4 shows a typical light response curve for ‘Hass’ avocado trees.
This information shows the light level at which leaf photosynthesis is optimal, called the light
saturation point. Beyond this point, there will not be an increase in photosynthesis regardless
of an increase in light level. Also, if a plant (or leaf) is not adapted to high light levels, PPF levels
above the light saturation point can damage the leaf.
Figura 4. Photosynthetic light response curve for ‘Hass’ avocado leaves (from Whiley, 1994).
25
20
A (µmol CO 2 m -2 s -1 ) 15
10
5
0
0 500 1000 1500 2000
s
PPF (µmol quanta m -2 -1 )
Universidad Autónoma de Chiapas